-
Risk Management
Our mature risk management system ensures that we can fulfill our mission to both help in alleviating the negative consequences of the risks that threaten societies and economies, while contributing to their solutions.

-
SCOR’s motto – “The Art & Science of Risk” – captures our approach, which combines the knowledge, expertise and experience of SCOR’s staff to respond to today’s risks and anticipate those of the future. For this, SCOR has:
- a skilled workforce, able to combine theoretical and analytical considerations with those that are more instinctive and based on practical experience;
- strong modelling capabilities and risk management tools to assess, quantify and actively manage SCOR’s risk profile.
-
The Expanding Risk Universe
The world is becoming increasingly unpredictable as the risk universe continues to expand. In response to this continually changing risk universe, SCOR uses a range of tools and mechanisms to manage its risk profile and anticipate emerging risks.
-
Managing SCOR’s Risk Profile
SCOR’s risk management team uses state-of-the-art modelling expertise and enterprise risk management (ERM) mechanisms to optimize SCOR’s risk profile.
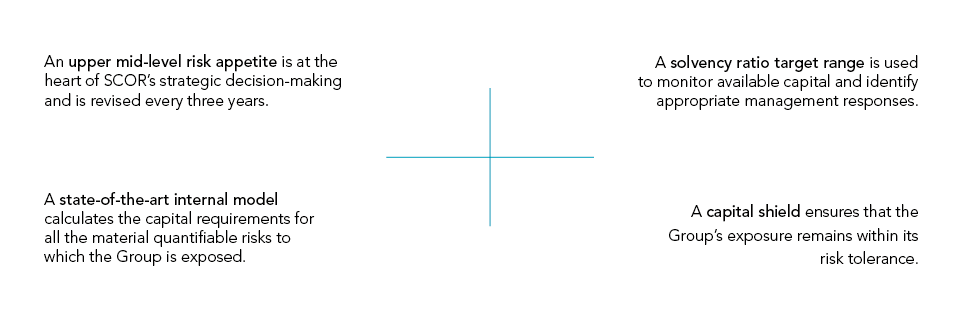
The risk management system is composed of two main parts:
the risk appetite framework, which defines the quantity and type of risks SCOR is willing to accept and sets risk tolerance limits;
the risk management mechanisms of the ERM framework, that ensure that the risk profile is optimized to maximize shareholder value within SCOR’s defined risk appetite.
SCOR's Risk Management Mechanisms
Risk Management is not only the domain of SCOR’s dedicated risk teams; a healthy “risk culture” is spread throughout the entire company thanks to initiatives that build awareness and understanding of risk-related issues. SCOR also provides mandatory training in ERM to new employees.
-
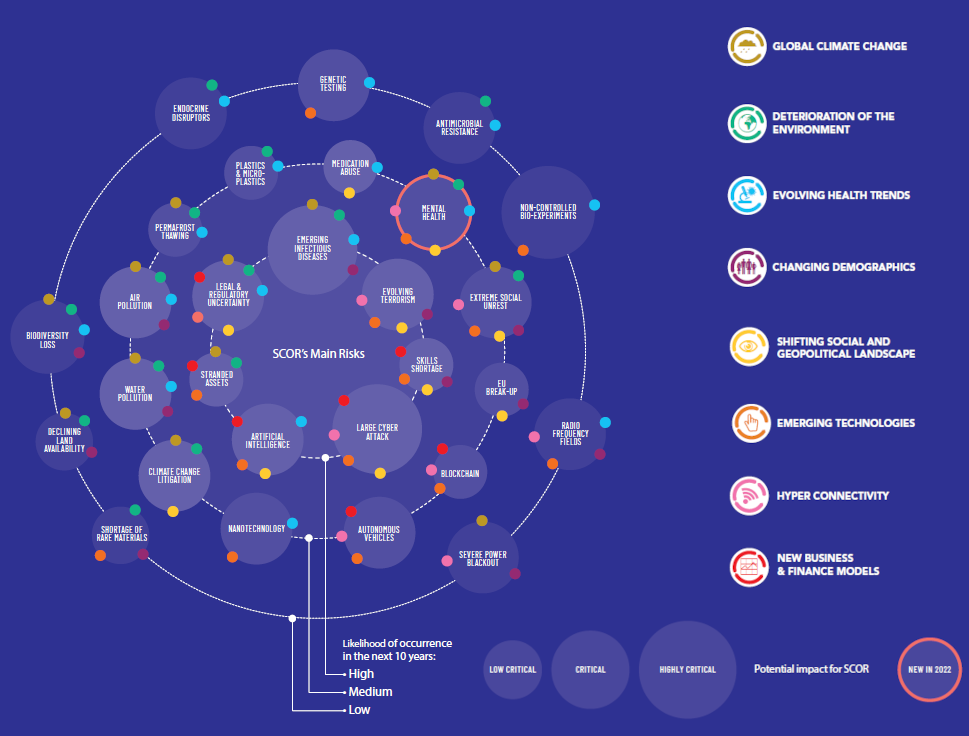
Anticipating Emerging Risks
SCOR has an Emerging risks process that is a formal part of the ERM framework. The process identifies new and rapidly changing risks and assesses their impacts on SCOR’s business (P&C and Life underwriting) and investments.

Assessments are also made in relation to the impact of identified risks on the Group’s operations and reputation. Risks are assessed by a transversal team, representing key SCOR activities.Everyone at SCOR is encouraged to participate in the identification of new emerging risks.
-
-
Managing Climate-Related Risks
SCOR is working towards a holistic assessment of climate risks and the exposure of its activities to them, including underwriting and investment activities, and SCOR’s own operations. SCOR’s approach to climate risk management includes:
- assessing climate-related risks and opportunities for the business;
- contributing to the understanding of climate-related risks, e.g. by developing and improving SCOR’s catastrophe modelling tools to better capture climate risks and through partnerships with scientific organizations for the modelling of climate events;
- analyzing the exposure of SCOR’s investment portfolio to both acute physical risks that could be impacted by climate change and to climate transition risks;
- contributing to the transition towards a lower-carbon economy through related insurance coverage products and investment in renewable energy projects;
- monitoring and progressively reducing the contribution of SCOR’s direct operations to Greenhouse gas emissions.
-
 Science At The Core of Risk Management
Science At The Core of Risk ManagementThe Group allocates significant resources to risk research and the dissemination of risk-related knowledge.
We invest in fundamental research and support the development of scientific risk management techniques in various disciplines. Since 2011, the SCOR Corporate Foundation for Science has devoted more than EUR 13 million to promoting scientific research.
Internally, SCOR conducts projects in conjunction with students from renowned universities and has developed partnerships with diverse academic/scientific institutions in various countries over the years.